Sexual Abuse Clinical Pathway — Emergency Department
Sexual Abuse Clinical Pathway — Emergency Department
Examination and Photodocumentation Guidance for SART/Sexual Abuse Evaluations
Diagnostic Quality
SCAN Team providers review images obtained during the anogenital exam.
To draw meaningful conclusions as to the presence or absence of findings, the set of photos must overall achieve diagnostic quality.
Definition of Diagnostic Quality – A set of photos that clearly shows:
| Female |
|
|---|---|
| Male |
|
Obtaining Images of Anogenital Area for SART /Sexual Abuse Evaluations
- Assign roles prior to the exam, including examiner and photographer
- If using Haiku, photographer should open child’s chart on phone prior to the examination
- Use the portable light in the SART Cart that can clip onto a phone; it should be used for every SART Exam
- Obtain images of the following as able:
- Vulva prior to labial traction — Start with a visual inspection of the vulva and note if there are findings before doing labial traction (e.g., rash, lesions, bleeding, discharge)
- Hymen with labial traction
- Anus with separation of the buttocks
- Obtain images even if exam is normal
- Hold camera ~12 inches or closer to the area and point directly at the subject
- Avoid angling the camera
- Aim to take 8-10 photos in total. Review as you go to confirm image quality, adjust positioning/lighting as needed
- If the structures are too small in the frame to visualize clearly, try moving the phone closer rather than zooming in on the phone screen
- For male anatomy, obtain photographs of the ventral and dorsal aspects of the penile shaft, glans, and prepuce (if present) as well as the anus
Instructions for Labial Traction
- In most patients with female anatomy, visualizing the hymen will not be achieved with labial separation (Figure 1) alone. Labial traction (Figure 2) should be used to visualize the hymenal rim in most patients.
- Labial traction is not painful in most patients regardless of pubertal status when done correctly.
- Two gloved hands are needed to perform the exam properly.
- Grasp the labia majora and minora bilaterally with the thumb and forefinger and pull the labia toward you while simultaneously separating the labia. Grasping the labia minora closer to the hymen and using out-and-downward traction is more likely to yield good visualization.
- The photographer can guide the examiner to change the degree or direction of traction that will optimize visualization.
Troubleshooting
- Raise the stretcher to a height that minimizes effort for the examiner and photographer.
- Putting a rolled blanket under the patient’s hips often improves visualization.
- If the hymen is folded over, ask the patient to reposition and/or cough (Valsalva).
- Another technique is to instill a few drops from a saline bullet to float the hymen.
- In postpubertal patients with redundant hymenal tissue, use a saline pre-moistened cotton-tipped applicator to pass under or behind the hymenal folds. This will allow you to confirm the presence (or absence) of normal tissue.
- Do not directly touch a prepubertal hymen with an applicator or any device as it can be very painful.
- It may be helpful to include a cotton-tipped applicator in photos to ensure there is photodocumentation of the complete rim of the hymen, or to illustrate a traumatic finding such as a hymenal transection.
- If other methods of hymen visualization are unsuccessful, have the patient lie prone with the knees tucked to the chest (Figure 3), which will make the hymen and vaginal canal easier to see. Keep in mind that this is an especially vulnerable position for the patient.
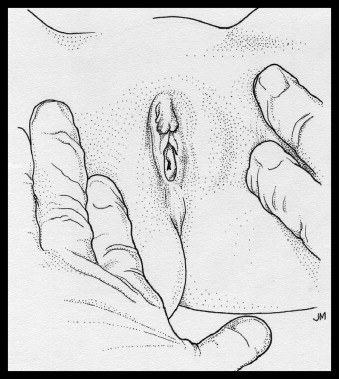
Figure 1
Supine labial separation method
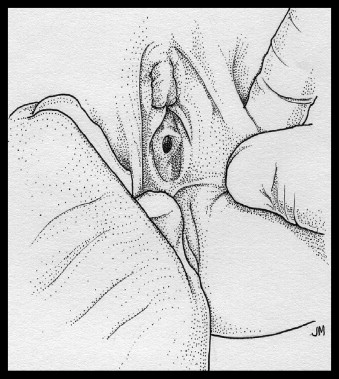
Figure 2
Supine labial traction technique
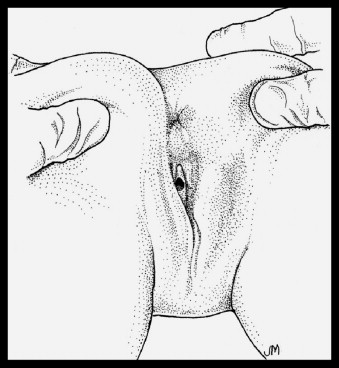
Figure 3
Prone knee–chest position
Reprinted from Cathy Boyle, John McCann, Sheridan Miyamoto, Kristen Rogers, Comparison of examination methods used in the evaluation of prepubertal and pubertal female genitalia: A descriptive study, Child Abuse & Neglect, Volume 32, Issue 2, 2008, Pages 229-243, ISSN 0145-2134, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2007.06.004, with permission from Elsevier.
Real-time SCAN Review of SART Photos
If you have questions about exam findings or about the diagnostic quality of the photos you are taking:
- Inform patient/family that you are stepping out of the room to talk with an offsite Child Protection Team specialist who will review the photos.
- Let the patient regain a position of comfort.
- Page the SCAN fellow on call to review your exam findings and discuss whether additional photos are needed to achieve diagnostic quality.
- Obtain additional photos if recommended by SCAN.
- The medical team can also clarify with SCAN how to describe and document certain anogenital findings based on photodocumentation.
References