Infants with Ankyloglossia (Tongue-Tie) Clinical Pathway — Outpatient Specialty Care and Primary Care
Infants with Ankyloglossia (Tongue-Tie) Clinical Pathway — Outpatient Specialty Care and Primary Care
Infant History and Physical Assessment
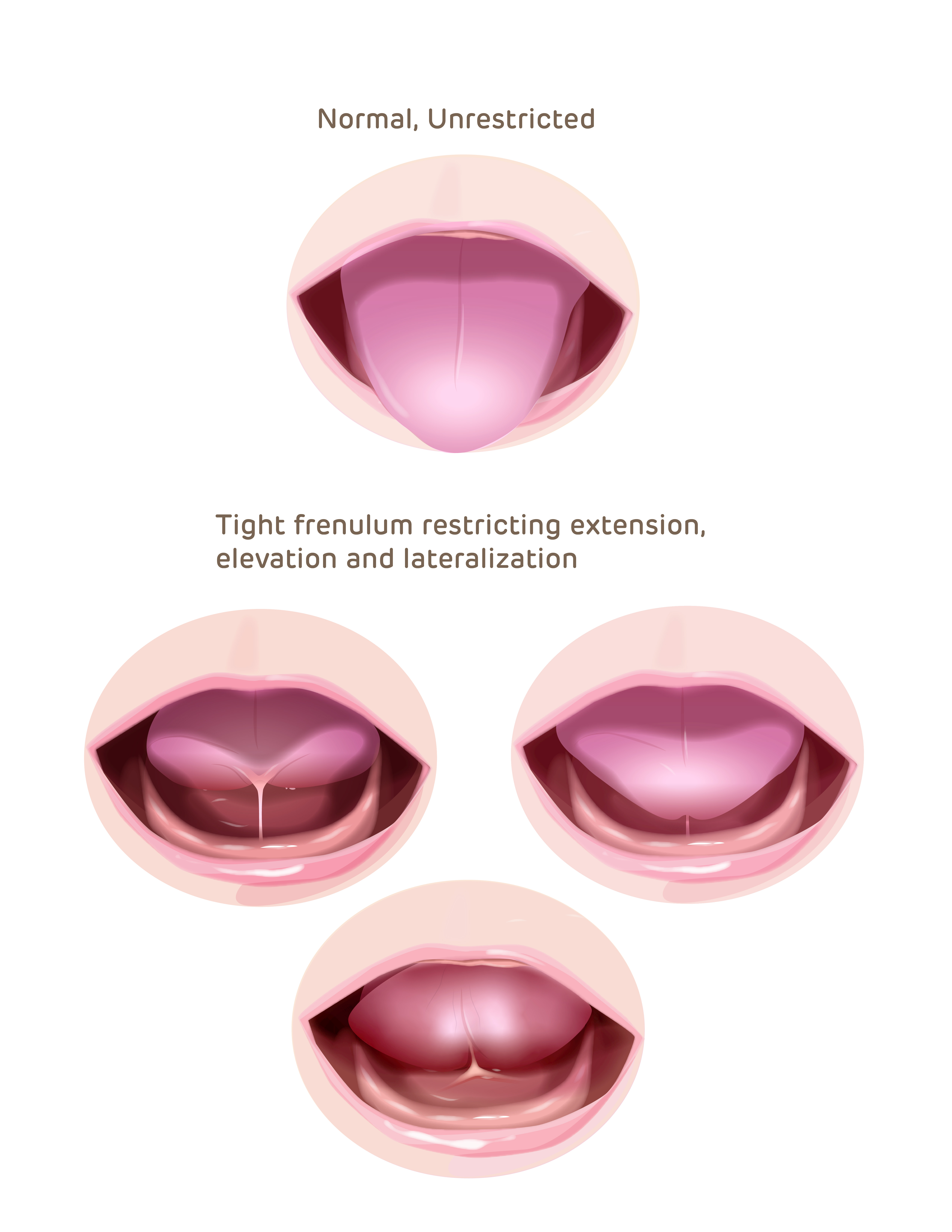
- A restrictive sublingual frenulum may cause significant functional impediment to:
- Infant latch, suckling
- Breast milk transfer
- Lactating parent nipple/areolar discomfort
- Trauma while breastfeeding
- Increased risk of discontinuing breastfeeding
- May result from multifactorial issues
- Musculoskeletal issues may interfere with successful breastfeeding. In such instances, referral to developmental motor therapist (PT/OT) may be beneficial.
- e.g., torticollis, head-flattening, increased or decreased tone (particularly of upper body or neck muscles)
| General |
|
|---|---|
| Feeding History |
|
| ENT |
|
| Oral Cavity |
|
Growth Assessment
Growth Charts
- Several growth charts available in EHR
- For most children, the appropriate growth chart will be the default
- WHO Child Growth Standards will be most appropriate
Post-natal Weight Gain
- Lose up to 10% of birth weight
- Regain birth weight by the first 2-3 wks of life
- Weight loss should cease by day 7 of life
| Age (corrected) | Median gm/day | |
|---|---|---|
| Females | Males | |
| 2-4 wks | 29 | 34 |
| 4 wks to 2 mos | 34 | 40 |
| 2-3 mos | 24 | 27 |
| 3-4 mos | 20 | 21 |
| 4-5 mos | 16 | 17 |
| 2-6 mos | 13 | 14 |
| 6-8 mos | 11 | 11 |
| 8-10 mos | 9 | 9 |
| 10-12 mos | 8 | 8 |
References
- WHO Child Growth Standards July 2010 (25th-75th%)
- Body Composition of Reference Children from Birth to Age 10 Years