Urticaria or Angioedema Clinical Pathway — Emergency Department and Primary Care
Urticaria or Angioedema Clinical Pathway — Emergency Department and Primary Care
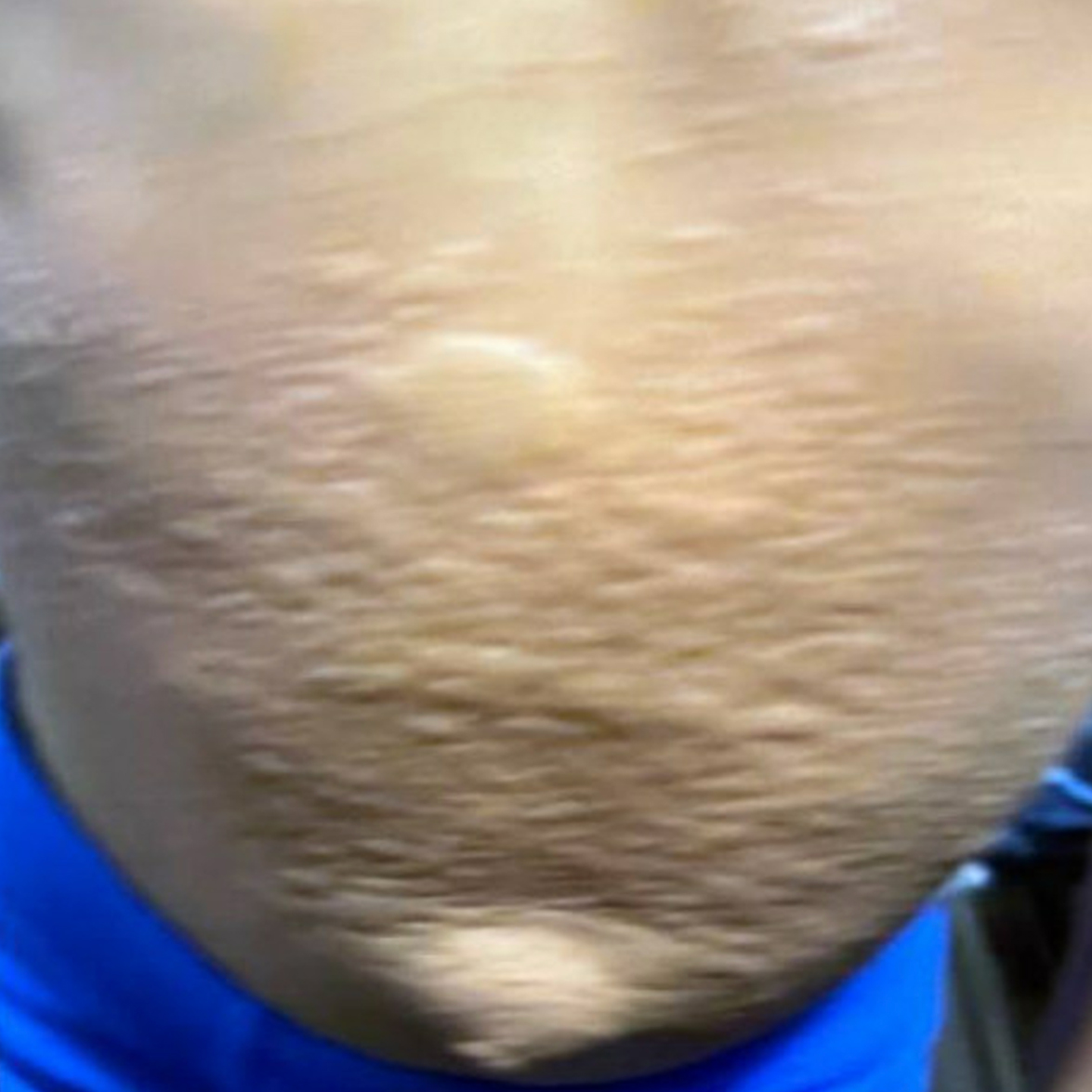
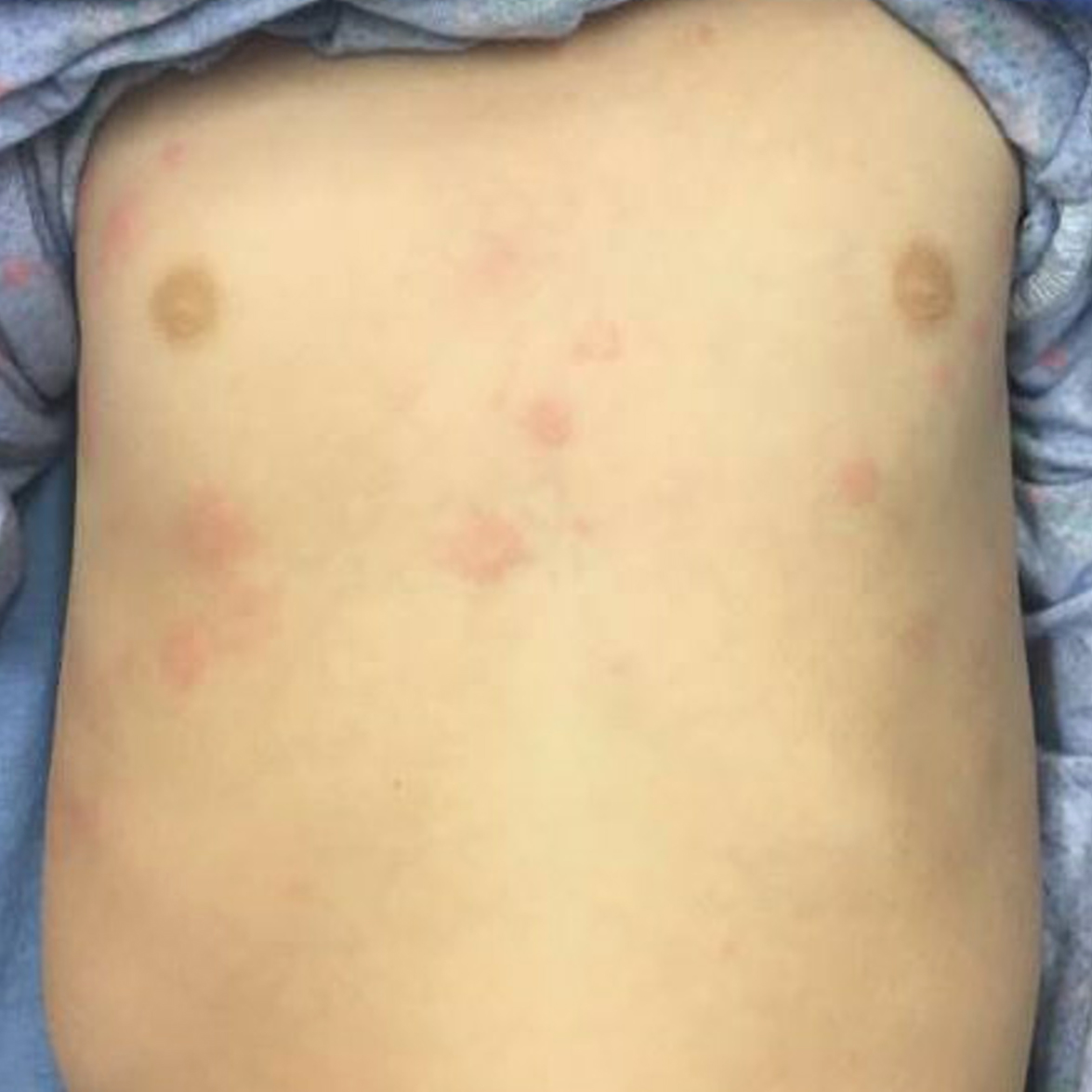
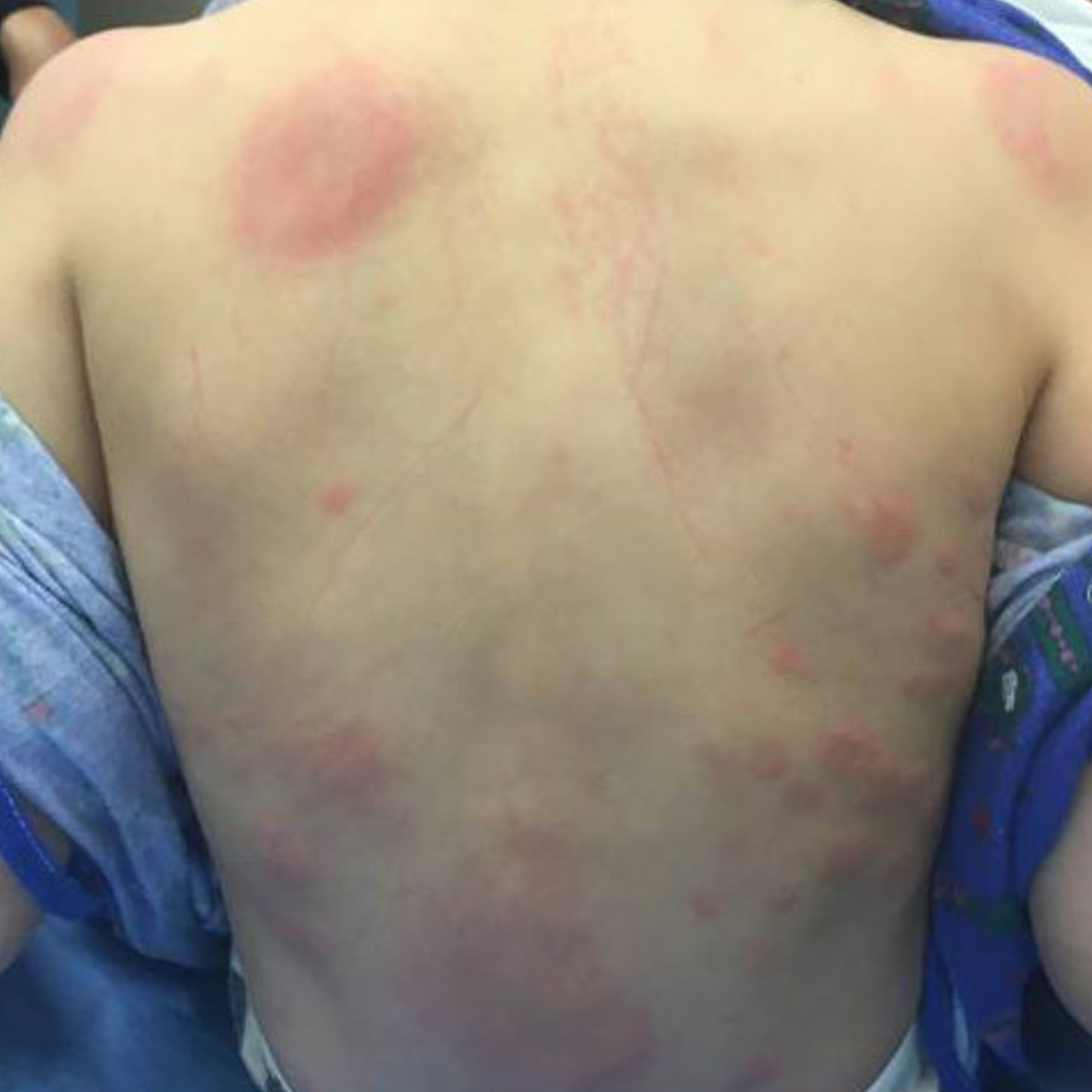
Urticaria
- Urticaria is erythematous, blanching lesions often with central clearing
- Individual lesions are transient and often lasting < 24 hrs, with associated pruritus
 |
 |
 |
 |
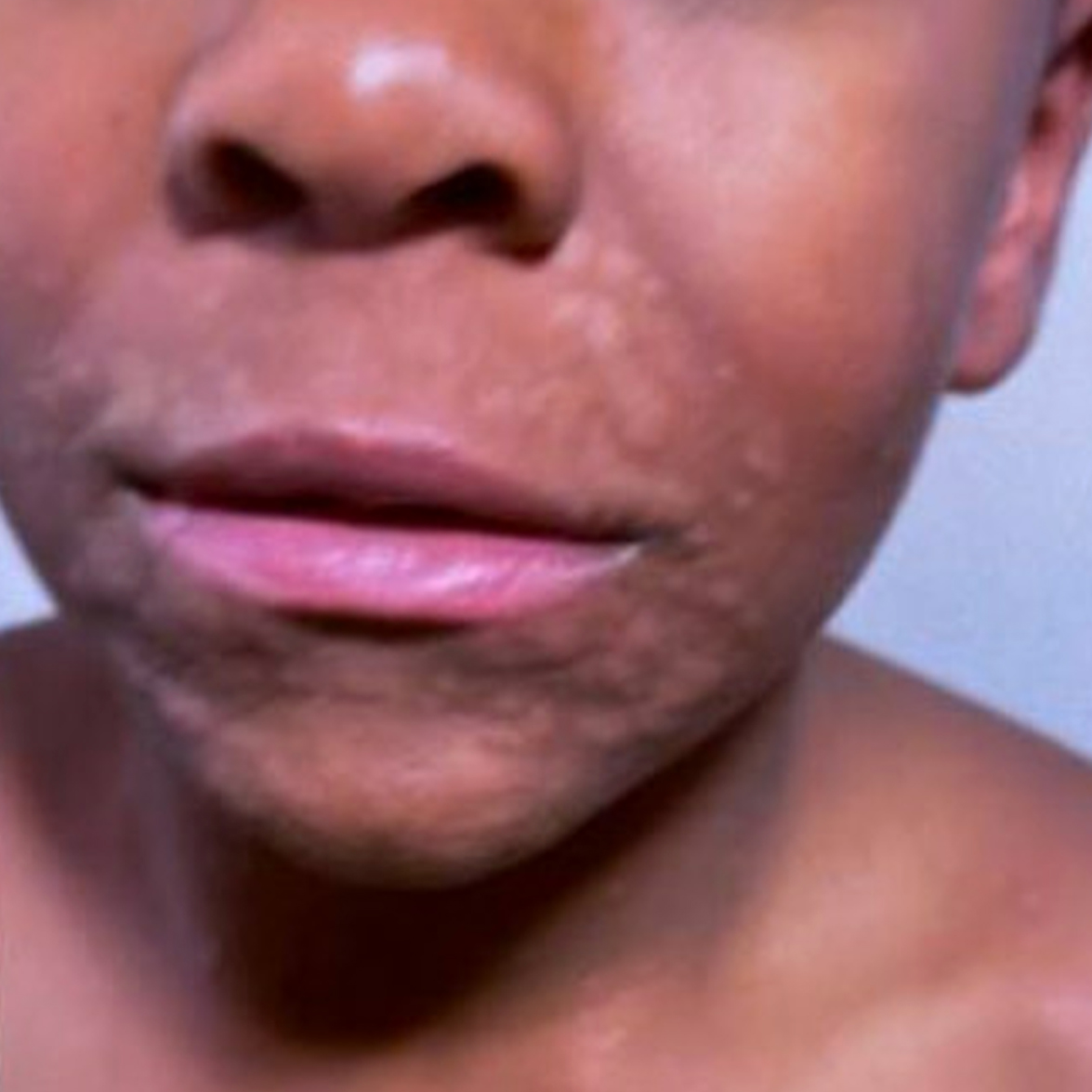
Angioedema
Angioedema is non-pitting edema of deep layers of the skin that commonly occurs in the eyelids, mouth or genitals.
| Angioedema Category | Features |
|---|---|
| Histamine Mediated More common |
|
| Bradykinin Mediated |
|