PHACE syndrome (posterior fossa defects, hemangioma, arterial anomalies, coarctation of the aorta and cardiac defects, eye abnormalities) is a constellation of findings of unknown etiology that has been described in a few hundred children worldwide. Diagnosis of this condition requires presence of large segmental hemangioma with at least one major criteria, including posterior fossa brain anomalies or other hypoplasia or dysplasia of the mid-brain or hindbrain.
The hemangioma will typically appear in the large facial segment shortly after birth. It can be progressive. It is usually treated by propranolol during the first year of life. Initiation of propranolol may require initiation in the neonatal ICU to monitor for safety. Long term, children with PHACE syndrome are at risk for developmental issues and epilepsy. In addition, they can have a progressive vascular disease that can lead to a stroke.
In utero diagnosis allows for early treatment
Abnormalities of the cerebellum is one of the most common referrals seen in the Richard D. Wood Jr. Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment (CFDT). During pregnancy, unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia can be detected during a 20-week anatomy scan. We use a multidisciplinary approach to counseling including review of history and imaging with radiology, neuroradiology, maternal-fetal medicine, neurology, neonatology and neurosurgery. While the majority of cases of unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia are not ultimately PHACE syndrome, careful evaluation for other signs of PHACE can be performed in utero.
I
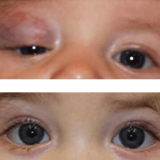
Image: (Top) Before treatment: 9-week-old boy with an eyelid/orbital lesion. (Bottom) After treatment: The same child at age 4 months, after 6 weeks of oral propranolol.
We have retrospectively analyzed all the children who ultimately were diagnosed as PHACE that were seen in the CFDT (nine patients) to determine what clues could have been found prenatally to more efficiently diagnose this condition. We have identified multiple findings to help detect future patients:
- Unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia consists of a cystic lesion with vermian hypoplasia
- Many of the patients will also have abnormalities of the fourth ventricle
- Half of the patients have cardiac or ocular findings in prenatal echocardiogram or fetal ultrasound
If children are suspected to have PHACE syndrome, they require early postnatal evaluation by Dermatology, Cardiology, Neurology, Neurosurgery and Ophthalmology for effectively managing symptoms. Repeat imaging after birth should include a brain MRI and MR angiography. Imaging can reveal evolution of a hemangioma prior to birth, unilateral tortuous intracranial vessels, or enlargement of Meckel’s cave from an evolving hemangioma. Repeat echocardiogram also needs to be performed to determine any changes in large vessels. Ultimately, one-third of the children have needed a ventriculoperitoneal shunt because of hydrocephalus.
Importantly, now that propranolol is the main treatment for the facial hemangioma, there appears to be a decreased incidence of stroke in the long-term in the few patients we have followed. Therefore, the earlier a diagnosis is made, we may have a chance to quickly intervene and reduce any long-term consequences.
Featured in this article
Specialties & Programs
PHACE syndrome (posterior fossa defects, hemangioma, arterial anomalies, coarctation of the aorta and cardiac defects, eye abnormalities) is a constellation of findings of unknown etiology that has been described in a few hundred children worldwide. Diagnosis of this condition requires presence of large segmental hemangioma with at least one major criteria, including posterior fossa brain anomalies or other hypoplasia or dysplasia of the mid-brain or hindbrain.
The hemangioma will typically appear in the large facial segment shortly after birth. It can be progressive. It is usually treated by propranolol during the first year of life. Initiation of propranolol may require initiation in the neonatal ICU to monitor for safety. Long term, children with PHACE syndrome are at risk for developmental issues and epilepsy. In addition, they can have a progressive vascular disease that can lead to a stroke.
In utero diagnosis allows for early treatment
Abnormalities of the cerebellum is one of the most common referrals seen in the Richard D. Wood Jr. Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment (CFDT). During pregnancy, unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia can be detected during a 20-week anatomy scan. We use a multidisciplinary approach to counseling including review of history and imaging with radiology, neuroradiology, maternal-fetal medicine, neurology, neonatology and neurosurgery. While the majority of cases of unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia are not ultimately PHACE syndrome, careful evaluation for other signs of PHACE can be performed in utero.
I

Image: (Top) Before treatment: 9-week-old boy with an eyelid/orbital lesion. (Bottom) After treatment: The same child at age 4 months, after 6 weeks of oral propranolol.
We have retrospectively analyzed all the children who ultimately were diagnosed as PHACE that were seen in the CFDT (nine patients) to determine what clues could have been found prenatally to more efficiently diagnose this condition. We have identified multiple findings to help detect future patients:
- Unilateral cerebellar hypoplasia consists of a cystic lesion with vermian hypoplasia
- Many of the patients will also have abnormalities of the fourth ventricle
- Half of the patients have cardiac or ocular findings in prenatal echocardiogram or fetal ultrasound
If children are suspected to have PHACE syndrome, they require early postnatal evaluation by Dermatology, Cardiology, Neurology, Neurosurgery and Ophthalmology for effectively managing symptoms. Repeat imaging after birth should include a brain MRI and MR angiography. Imaging can reveal evolution of a hemangioma prior to birth, unilateral tortuous intracranial vessels, or enlargement of Meckel’s cave from an evolving hemangioma. Repeat echocardiogram also needs to be performed to determine any changes in large vessels. Ultimately, one-third of the children have needed a ventriculoperitoneal shunt because of hydrocephalus.
Importantly, now that propranolol is the main treatment for the facial hemangioma, there appears to be a decreased incidence of stroke in the long-term in the few patients we have followed. Therefore, the earlier a diagnosis is made, we may have a chance to quickly intervene and reduce any long-term consequences.
Contact us
Richard D. Wood Jr. Center for Fetal Diagnosis and Treatment