Post-Hemorrhagic Hydrocephalus in Pre-Term Infants Clinical Pathway — N/IICU
Post-Hemorrhagic Hydrocephalus in Pre-Term Infants Clinical Pathway — N/IICU
Measuring Ventricular Size on Cranial Ultrasound
Research shows that images obtained using ultrasound are as clinically useful as those obtained using CT or MRI. Cranial ultrasound from referring hospitals should include both of the following measurements when possible.
Frontal-Occipital Horn Ratio (FOR)
FOR = (A+B)/2C and is calculated using the labeled measurements.
- A = Widest distance across frontal horns (at level of foramen of Monro)
- B = Widest distance across occipital horns (FOR)
- C = Widest biparietal diameter
Calculate FOR on multiple slices, and use maximal FOR for clinical decision making.
FOR widest value for each can be on different images
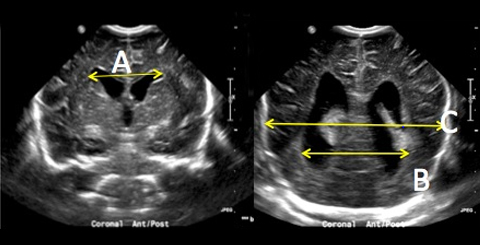
*from CORONAL cine’ loops
Normative Absolute Values
- Normal = 0.4
- Mild HC = 0.55
- Moderate HC = 0.60
- Severe HC = 0.7
- Good inter-rater reliability (> 0.9)
Frontal and Temporal Horn Ratio (FTHR)
FTHR = A+B/2C
- A = Widest distance across frontal horns
- B = Widest distance across temporal horns
- C = Broadest skull diameter at level of foramen Monro
Correlates highly with volumetric determinations
FTHR all measured at foramen of Monro in one image
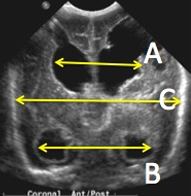
*from CORONAL cine’ loops