| Induction and Maintenance |
- Inhalational induction and maintenance acceptable
- Consider IV induction teenagers and adults
- Boluses:
- Propofol 2-3 mg/kg, two syringes
- Fentanyl 1-3 mcg/kg
- Additional boluses available for maintenance as needed
- Lidocaine 1.0-1.5 mg/kg
- Consider for IV induction
- Vecuronium 0.1 mg/kg
- Do not re-dose to allow for sciatic nerve monitoring
- Methadone 0.1 mg/kg, max 10 mg
- Dispensed as a 10 mg/ml syringe
- Tranexamic acid 30 mg/kg over 10 min, max 2,000 mg
|
- Infusions for TIVA, if applicable
- Propofol 100-250 mcg/kg/min
- Remifentanil 0.1-0.2 mcg/kg/min
|
Airway Management
and Positioning Considerations |
- Standard oral tube
- Check all pressure points, especially arms and eyes
|
| Vascular Access |
- Peripheral IV x 2
- Arterial line is typically not needed
|
| Antibiotics |
Perioperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis |
| Analgesia |
- Methadone IV 0.1 mg/kg, max 10 mg
- Contraindicated for history of prolonged QT
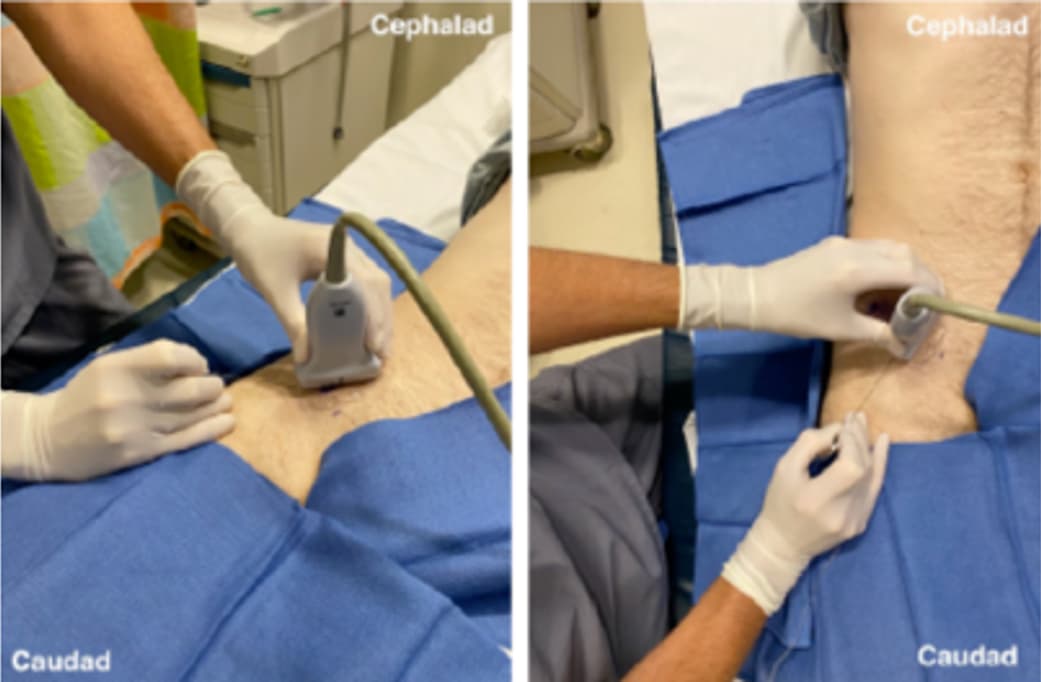
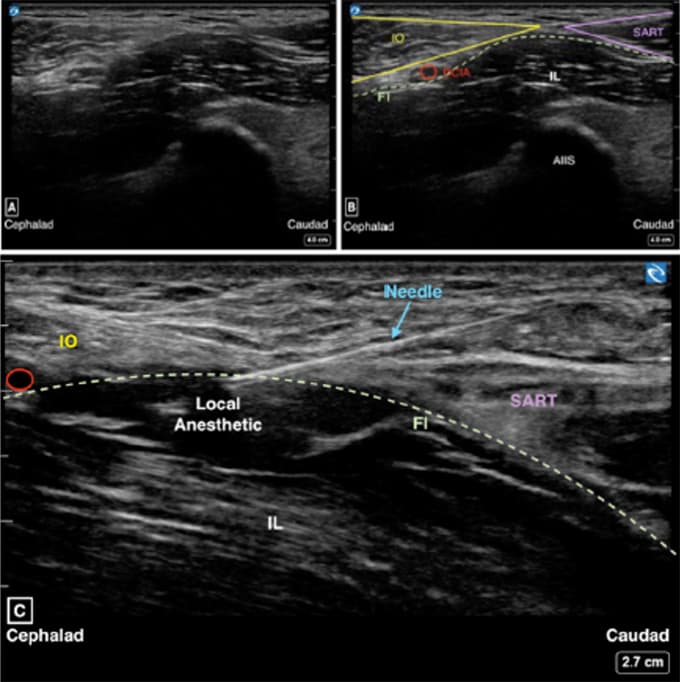
- Perform ultrasound-guided suprainguinal fascia iliaca block
- Initiate block with bolus of:
- Ropivacaine 0.2% 30-40 mL, max 1 ml/kg and
- Clonidine 1-2 mcg/kg, max 100 mcg
- Administer at skin closure:
- Acetaminophen IV 15 mg/kg, max 1,000 mg
- Ketorolac 0.5 mg/kg, max 30 mg
- Surgeon may infiltrate 10-20 mL of local anesthesia (ropivacaine or bupivacaine) into periosteum and wound at case closure. Dosing occurs about 4 hrs after initial fascia iliaca block.
|
| Anti-emetic Prophylaxis |
- Pre-incision: Dexamethasone 0.1-0.2 mg/kg IV, max 10 mg
- At case conclusion: Ondansetron 0.1 mg/kg IV, max 4 mg
|
| Fluid Management |
- Avoid excessive crystalloid administration
- Consider lactated ringers 3 ml/kg/hr
- Bolus 10 mL/kg lactated ringers for intraoperative hypotension
|
| Laboratory Testing |
- Point of care testing not typically needed
- Consider ABG, HemoCue, or CBC for unexpected bleeding
|
| Hemodynamic Goals |
Maintain SBP within 20% of baseline
|
| Ventilation Strategy |
- TV: 6-8 mL/kg based on ideal body weight
- PEEP: 5cmH20
- Reduce FiO2 < 30% with goal of SpO2 > 95%
|
| Transfusion and Blood Conservation Guidelines |
- Ensure 1-unit PRBCs autologous or donor available before start of case
- Antifibrinolytic management:
- Tranexamic acid bolus: 30 mg/kg over 10 min, max 2,000 mg before incision
- Tranexamic acid infusion: 10 mg/kg/hr
- Cell saver arranged by surgery
- Blood loss can range from 500-1,000 mLs, transfusion rarely required
- Maintain hemoglobin > 7 g/dL
- Discuss transfusion plan with surgery team when indicated
|
| Emergence |
- Neurological examination not required before transport to PACU
- Awake or deep extubation acceptable
|