Cellulitis/Abscess Clinical Pathway — Emergency Department and Inpatient
Distinguishing Cellulitis from Inflammation Associated with Subcutaneous Abscess
Differentiating cellulitis from normally expected inflammation associated with an abscess can be difficult, given that both may have an erythematous appearance. Cellulitis is described as a subcutaneous abscess with surrounding inflammation, and should not be used to describe cutaneous inflammation associated with underlying collections of pus.
Subcutaneous abscesses frequently have a central papule or pustule that is surrounded by erythematous swelling. This distinction is important, given that the treatment for cellulitis is an antibiotic, while the treatment for an abscess is incision and drainage. Most abscesses do not have overlying cellulitis; however, if an abscess has marked erythema that extends beyond the area of induration, the diagnosis of cellulitis is appropriate.
Tips for Interpreting Physical Exam Findings
Abscess with Papule with
Surrounding Inflammation
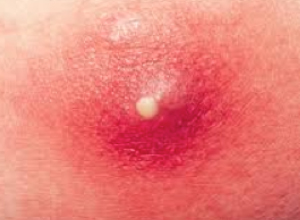
Photo courtesy of Health Blog (healthyone.org)
Abscess with Associated Cellulitis
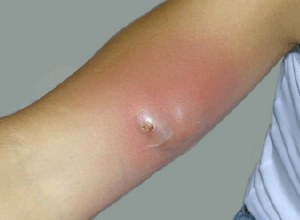
Photo courtesy of HIV Web Study at the University of Washington
Tips for Interpreting Ultrasound
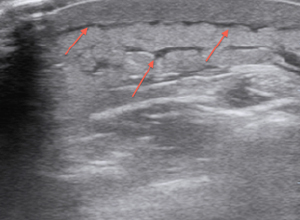
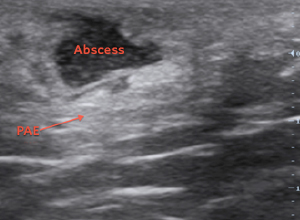
The ultrasound findings of an abscess include a hypoechoic (black) area with thickening of the surrounding subcutaneous tissue compared to the normal surrounding tissue. Irregular borders are often seen in early stages of formation. They progress to more well-circumscribed borders seen in later stages. Train your eye to look for an ultrasound artifact posterior/deep to the abscess called posterior acoustic enhancement (PAE), where the tissue is hyperechoic (more white) compared to the surrounding tissue. Sometimes by applying gentle pressure with the probe and then releasing, you will see the pus “swirling” around within the abscess cavity, a phenomenon known as the “squish sign.” With cellulitis, the ultrasound image has the appearance of “cobblestoning” with the edema (hypoechoic/black areas) tracking within the septations of the subcutaneous tissue (see arrows).
Abscess
Cellulitis