What is pilomatrixoma?
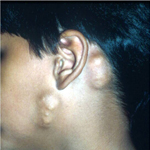
A pilomatrixoma is small, hard mass found under the skin. It most commonly presents as a single lump found on the face or neck. However, multiple masses may be found.
Pilomatrixoma can also be found on the scalp, eyelids, and arms.
Most cases of pilomatrixoma occur in children younger than 10, but are also seen in older children and young adults. Females are twice as likely as males to have a pilomatrixoma.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a pilomatrixoma include a small, hard mass less than 3 cm in diameter, typically covered by normal-appearing skin. The mass is usually painless unless it becomes inflamed or infected.
A pilomatrixoma forms when cells abnormally harden and form a mass under the skin. The cells involved are similar to hair follicle cells.
Diagnosis
A pilomatrixoma is diagnosed by physical examination.
Treatment
A pilomatrixoma will not go away or become smaller; therefore, surgical excision is the treatment of choice.
Removal of a pilomatrixoma is a day surgery, meaning your child will go home the same day as the procedure. The mass will be removed and sent to the lab to confirm the diagnosis.
Follow-up care
Your child will need to return to clinic about 2-4 weeks after surgery.
Recurrence rates after surgical excision of pilomatrixoma are low, but patients should be monitored to ensure the lesion does not return.
Why choose CHOP for your child's surgery
If your child needs surgery, you want to know their care is in the hands of the best, most compassionate team. CHOP's world-class pediatric surgeons and experienced staff are here for you.

Preparing for surgery
Find tips to prepare for your preoperative visit with CHOP’s pediatric general surgeons, and resources to help prepare your child for surgery.
Resources to help
Division of Pediatric General, Thoracic and Fetal Surgery Resources
We have created resources to help you find answers to your questions and feel confident with the care you are providing your child.
