Overview
Our Clinical Pathways Program within the Center for Healthcare Quality & Analytics aims to incorporate evidence, best practice, and local expert consensus into easily accessible, shared mental models for use by clinical teams at the point of care to facilitate the delivery of high-quality medical care.
Meet Our Team

Medical Director
Jane Lavelle, MD

Program Manager
Becca Kasper, RN

Associate Medical Director
Brandon Ku, MD

Improvement Advisor
Pamela Wentz, RN

Improvement Advisor
Kathy Houng, CRNP

Improvement Advisor
Nina Capoferri, RN, BSN

Senior Interactive Designer
Stephen Crawford, BS

Physician Partner, Hospital Medicine
Emily Roumm Kane, MD, MS

Physician Partner, ICU
Heather Wolfe, MD

Physician Partner, Primary Care
Joshua Sperling, MD
Podcast and Videos
Explore pediatric-focused podcasts and educational videos from Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, featuring expert discussions aligned with CHOP's clinical pathways on topics like asthma, pneumonia, constipation, and more.
Publications
Clinical Pathways at Children's Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have an impact on patient care. Here is a list of relevant publications.
Contact Us
Reach out with questions about any of the clinical pathways featured on this site or about our pathway development approach.
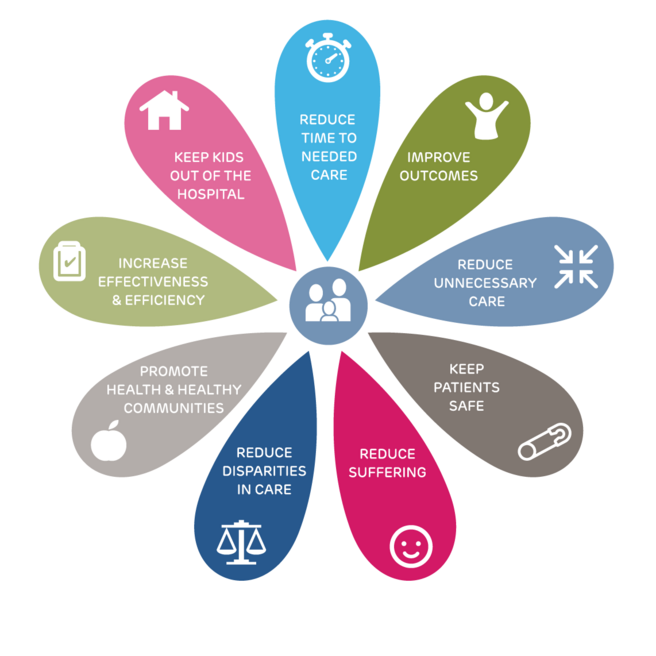
Connecting Pathways to Quality Impacts
Clinical pathways are structured, evidence-based care plans designed to standardize treatment, reduce variability, and ensure timely, effective interventions. By aligning care with best practices, clinical pathways help improve outcomes, enhance safety, reduce unnecessary services, and promote health equity—directly supporting our quality impact themes shown here.